what is AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration)
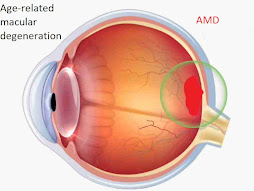 |
| What is AMD? |
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common eye condition that can affect people as they get older. The macula is the central part of the eye that makes it possible to see fine detail and color. AMD is a disease that damages the macula, causing a loss of vision in the center of the visual field. Due to this disease, it is not visible clearly, due to which there is a problem in reading, writing and driving etc.
What causes of AMD?
The exact cause of AMD is still unknown, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors can contribute to the development of the disease. With the increasing age of a person, the risk of developing this disease also increases. One of the primary causes of AMD is the buildup of waste products called drusen in the retina. Drusen are yellow deposits that accumulate between the layers of the retina and can interfere with the function of the cells that process visual information. Over time, the accumulation of drusen can lead to damage to the macula, which is the part of the retina responsible for central vision.
Another factor that can contribute to the development of AMD is inflammation. Chronic inflammation in the body can cause damage to the retina and lead to the formation of abnormal blood vessels that can leak fluid and blood into the macula. This type of AMD is called neovascular AMD and is more severe than the non-neovascular form. Genetics also play a role in the development of AMD. Researchers have identified several genes that are associated with an increased risk of AMD.
There are two types of AMD:-
Dry and wet. Dry AMD is the more common type, accounting for about 85-90% of cases. It is caused by the gradual breakdown of cells in the macula, leading to a slow and progressive loss of vision. Whereas, in the eye with wet AMD, there is an uncontrolled growth of blood vessels in the macula. These blood vessels can leak fluid and blood, leading to a rapid loss of vision.
What are the symptoms of AMD?
 |
| Symptoms of AMD |
This leads to degeneration of the macula, a major part of the retina of the eye. Because of this, central vision is maintained. Macular degeneration can cause problems with tasks such as reading, writing and driving.
- Blurred or distorted vision: One of the most common symptoms of macular degeneration is blurred or distorted vision. In such a situation, if a person sits down to read, then the lines are seen to be horizontal or wavy.
- Dark or empty spaces: Another common symptom of macular degeneration is the appearance of dark or empty spaces in the center of your vision. These spaces can make it difficult to see objects clearly and can also affect your ability to perceive depth.
- Reduced color perception: People with macular degeneration may experience a reduction in their ability to perceive colors. Colors may appear less vibrant, and it may be difficult to differentiate between different shades and hues.
- Difficulty adapting to low light: People with macular degeneration may find it difficult to adapt to low light conditions. This can make it challenging to see in dimly lit rooms or when driving at night.
- Need for brighter light: People with macular degeneration may also require brighter light than usual to see objects clearly. This may involve using brighter lamps or increasing the brightness on electronic devices.
- Decreased central vision: Macular degeneration directly attacks the blood vessels of the retina, causing loss of central vision.
How is AMD diagnosed?
 |
| Diagnose AMD |
- Visual acuity test: Measures how well you can see at a distance and up close.
- Dilated eye exam: Allows the eye doctor to examine the retina and macula for signs of AMD.
- Amsler grid test: Measures any distortion in your central vision.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT): Uses light waves to create detailed images of the retina and macula.
If the patient is diagnosed with wet AMD, the doctor does a fluorescein angiogram test. In this method, the dye is injected into the arm and carried to the blood vessels of the eye and pictures of the dye are taken with the help of a special camera.
How is AMD treated?
 |
| Treatment of AMD? |
(1) Anti-VEGF injections
(2) Laser therapy
(3) Photodynamic therapy
(4) Low vision aids
(5) Lifestyle changes
Treatment for dry macular degeneration
(1) Nutritional supplements
(2) Lifestyle changes
- Quitting smoking: Macular degeneration is aggravated by smoking so it should be quit as soon as possible.
- Eating a healthy diet: A diet low in saturated fat, processed foods, and plenty of fruits and vegetables can prevent the risk of macular degeneration.
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise reduces inflammation and improves circulation. The progression of macular degeneration stops.
(3) Anti-VEGF therapy
(4) Low vision aids
Macular degeneration causes and risk factors
- Age: Macular degeneration is more common in people over the age of 50, and the risk increases with age.
- Genetics: Some forms of macular degeneration have been linked to specific genes, and the condition may run in families.
- Smoking: Smoking has been identified as a significant risk factor for macular degeneration, and people who smoke are at a higher risk of developing the condition.
- Obesity: If a person has this disease then obesity can be harmful for him.
- Cardiovascular disease: People who have heart disease due to high cholesterol or high blood pressure in their body, the possibility of its spread increases.
- Sunlight exposure: Chronic exposure to sunlight, especially ultraviolet (UV) radiation, has been linked to an increased risk of macular degeneration.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop macular degeneration.
Supplements for macular degeneration
- Vitamin C and E: These antioxidants can help protect the eyes from free radicals, which can cause damage to the macula. Studies have shown that high doses of vitamin C and E can reduce the risk of developing macular degeneration.
- Zinc: Zinc is an important mineral for eye health and can help reduce the risk of macular degeneration. It is also believed to help with the absorption of other nutrients, such as vitamin A.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil, these fatty acids are important for overall health and can help reduce inflammation in the body. Inflammation is believed to play a role in the development of macular degeneration.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: These antioxidants are found in high concentrations in the macula and can help protect against damage from blue light.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is important for overall health and can help reduce inflammation in the body. It can also reduce the risk of AMD.
Prevention from age-related macular degeneration
- Eat a healthy diet: A healthy diet is essential for maintaining good eye health. Eating foods rich in antioxidants helps the macula stay healthy. And this food item includes fish, berries and green vegetables and fruits. Eating a diet that is high in saturated fats, on the other hand, has been linked to an increased risk of AMD.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise is important for overall health and can also help reduce the risk of AMD. Studies have shown that people who engage in moderate exercise, such as walking or cycling, have a lower risk of developing this eye disease.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can increase risk factor for AMD. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can damage the macula and increase the risk of developing this condition.
- Protect your eyes from the sun: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can increase the risk of AMD. Wearing sunglasses that block out UV radiation and a hat with a brim to shade your eyes can help protect your eyes from the sun.
-min.png)
-min.png)